MgtPro_9_MonteCarlo
Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo simulation is a method in the risk analysis and evaluation of engineering projects. It is a quantitative analysis method. When the number of random variables input in the project evaluation is more than three, there may be three or more states in each input variable. Monte Carlo simulation techniques should be used.
The principle of this method is to use a random sampling method to extract the values of a set of input variables, and calculate the project evaluation index based on the numerical values of the input variables. Through a large number of simulations of tens of thousands or even millions of times, the final evaluation is obtained. The probability distribution of the indicator and the cumulative probability distribution map, expected value, variance, and standard deviation, and the probability that the calculation item will change from feasible to infeasible, thereby estimating the risk assumed by the project investment.
General steps for Monte Carlo simulation
Select a random variable, the variable that is most sensitive to the net present value.
Determine the probability distribution of random variables
Extract random numbers for each random variable
Convert the extracted random number into the sampled value of each input variable
The sampled values constitute a set of project evaluation basic data
Calculate the value of the evaluation index under a random condition based on the basic data.
Repeat the above process and perform repeated simulations to obtain multiple sets of evaluation index values.
Organize the expected value, variance, standard deviation, probability distribution and cumulative probability distribution of the evaluation indicators obtained from the simulation results, draw the cumulative probability map, and at the same time, check whether the simulation times meet the predetermined accuracy requirements.
Based on the above results, the impact of each random variable on project revenue is analyzed.
Sample:
The time of the total construction period is estimated based on historical data simulation of each stage.
- According to the elements we divide in WBS, select random variables as four processes of software development: requirements engineering, design, development, testing
The total duration is the sum of the four processes
- Determine the probability distribution of random variables
According to historical data, pessimistic estimates, general estimates and optimistic estimates of each variable are obtained. It is assumed that the random variables obey the Gaussian distribution and the parameters of the Gaussian distribution are determined from the historical data.
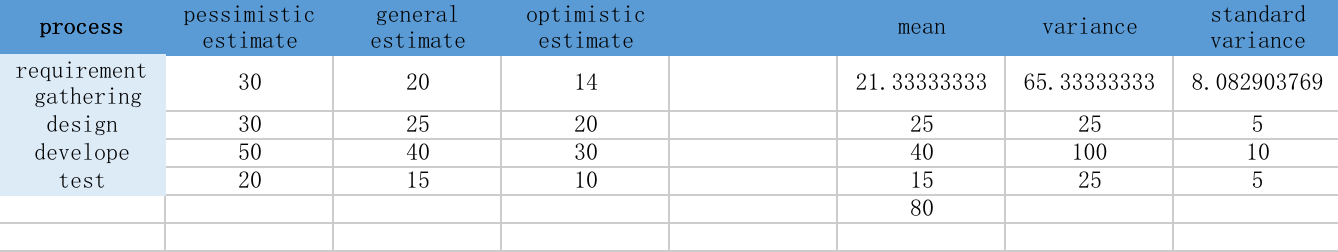
All variable are distributed as Gaussian distribution.
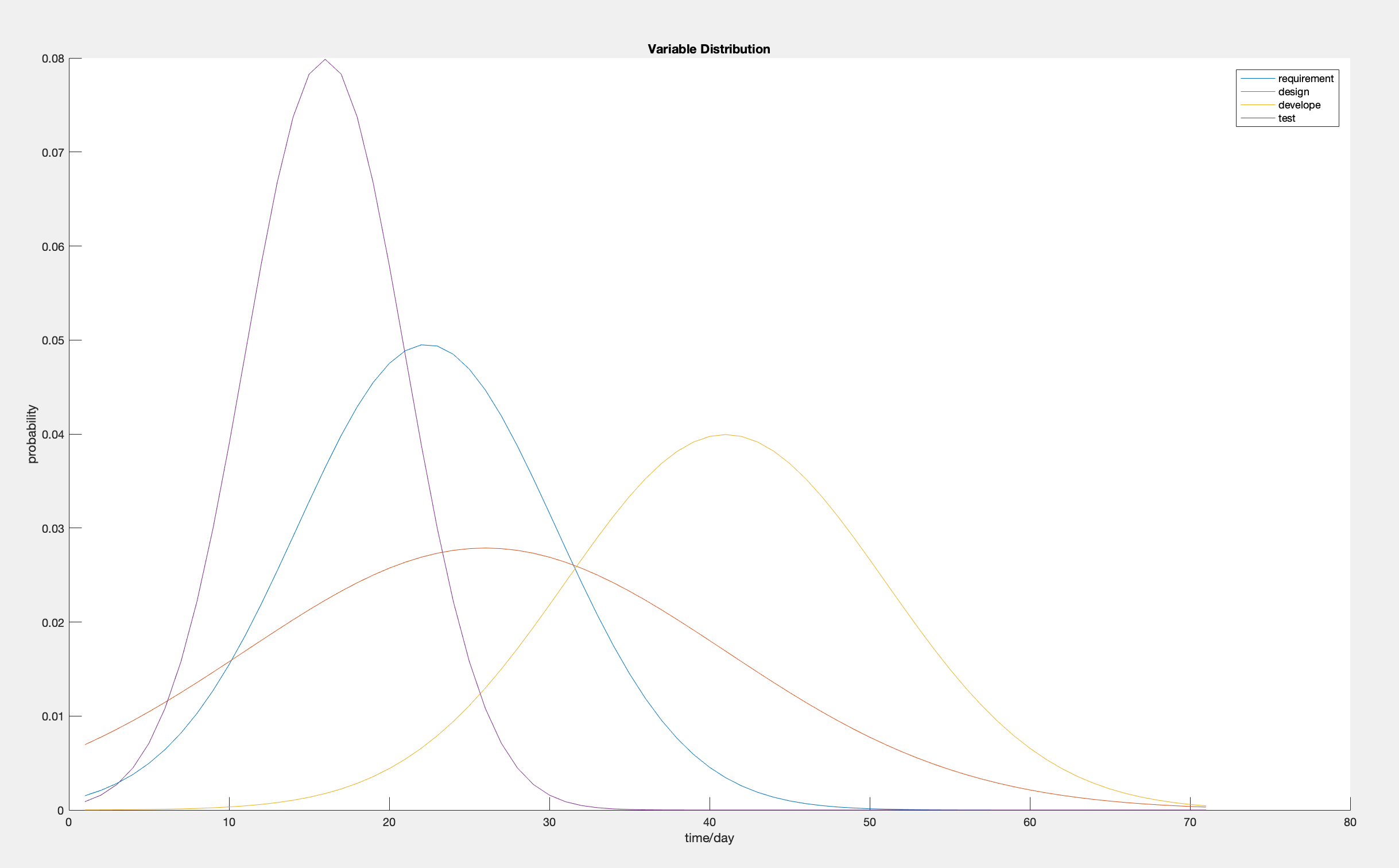
Extract random numbers for each random variable
Convert the extracted random number into the sampled value of each input variable
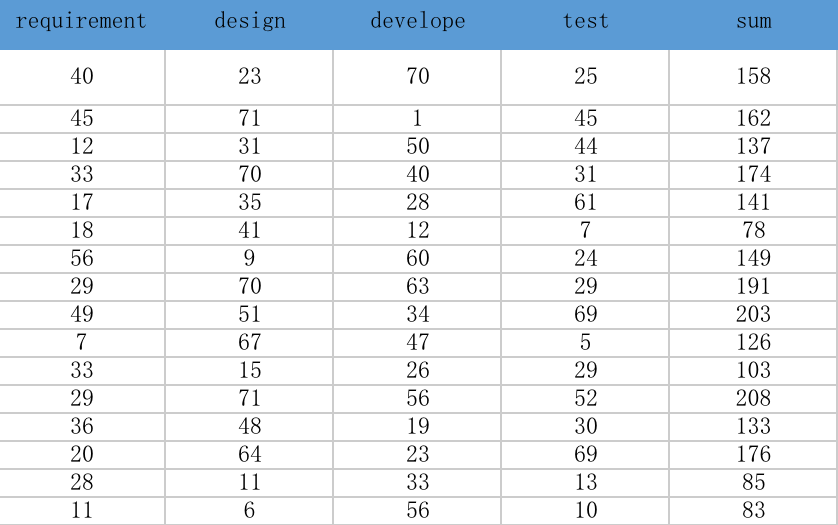
The sampled values constitute a set of project evaluation basic data
Calculate the value of the evaluation index under a random condition based on the basic data.
Repeat the above process and perform repeated simulations to obtain multiple sets of evaluation index values.
Organize the expected value, variance, standard deviation, probability distribution and cumulative probability distribution of the evaluation indicators obtained from the simulation results, draw the cumulative probability map, and at the same time, check whether the simulation times meet the predetermined accuracy requirements.
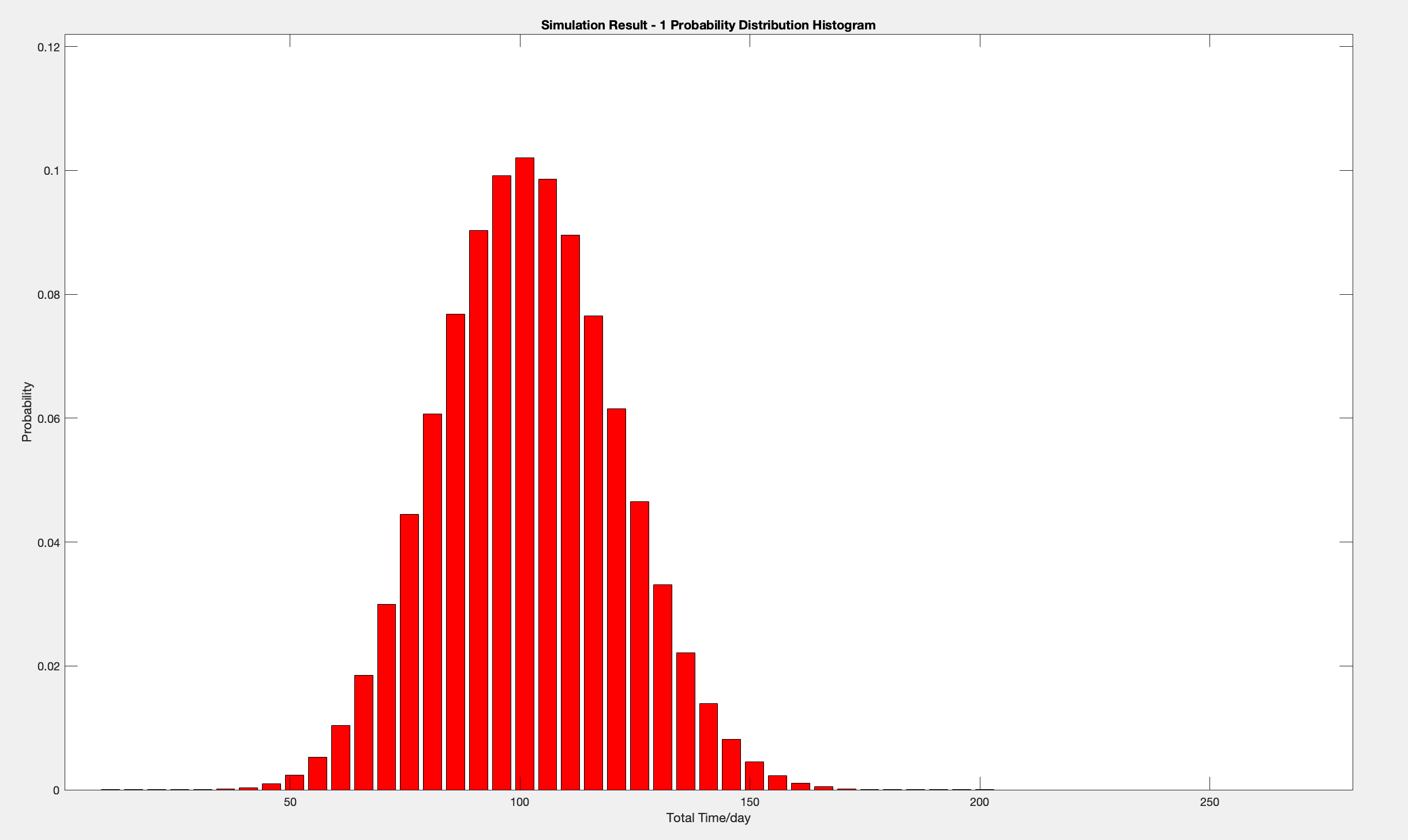
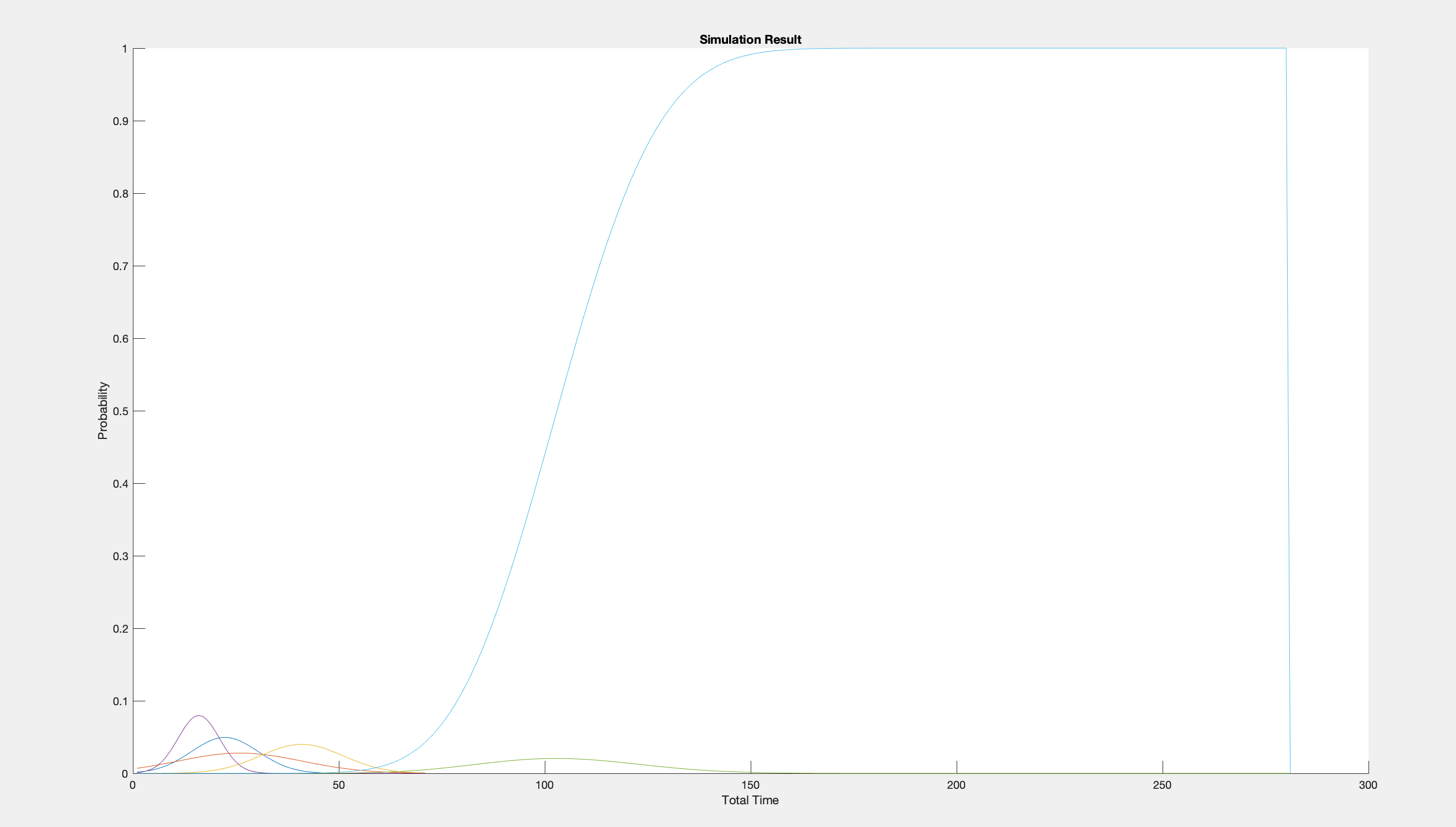
| Ex | StandVar |
|---|---|
| 103.8 | 19.2 |

